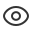
磁盘/分区/文件格式/文件系统/目录树
磁盘是用来存储数据的。
为方便管理、提高效率和安全性等,会把磁盘划分成多个磁盘分区。
每个磁盘分区可以有自己的文件格式,比如EXT3.
文件系统是用来管理文件的,不同文件系统(比如EXT2、NTFS等)格式不同。
文件系统跟目录树密切相关,linux文件系统的组织方式就是一颗目录树。
目录树的不同目录,可以挂载(mount)到不同的分区(partition),不同的分区可以有不同的文件格式。
df:查看系统存储空间使用情况
如下,使用df来查看系统存储空间使用情况,这里的单位是kb。
[root@VM_70_229_centos ~]# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 51474044 1305056 47531240 3% /
devtmpfs 503736 0 503736 0% /dev
tmpfs 508996 24 508972 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 508996 8488 500508 2% /run
tmpfs 508996 0 508996 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/vdb5 1998672 43492 1833940 3% /data/github
可以加上-h,容量的展示更直观些。
[root@VM_70_229_centos ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 50G 1.3G 46G 3% /
devtmpfs 492M 0 492M 0% /dev
tmpfs 498M 24K 498M 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 498M 8.3M 489M 2% /run
tmpfs 498M 0 498M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/vdb5 2.0G 43M 1.8G 3% /data/github
fdisk:查看未挂载/格式化的分区
运行如下命令,可以看到,除了/dev/vda1、/dev/vdb5,还有未挂载的分区。
[root@VM_70_229_centos ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/vda: 53.7 GB, 53687091200 bytes, 104857600 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000c47d9
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vda1 * 2048 104857599 52427776 83 Linux
Disk /dev/vdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xeb9c2fe3
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vdb2 4196352 20971519 8387584 5 Extended
/dev/vdb4 2048 4196351 2097152 83 Linux
/dev/vdb5 4198400 8392703 2097152 83 Linux
Partition table entries are not in disk orde
mount:挂载分区到目录
命令非常简单,如下,将/dev/vdb4挂载到了hello下。
mkdir hello
mount /dev/vdb4 hello
注意,如果/dev/vdb4还没格式化的话,上面命令会出错,提示文件系统未知。
mount: /dev/vdb4 is write-protected, mounting read-only
mount: unknown filesystem type '(null)'
出现这种情况的话,格式化一下就行。比如格式化成EXT3文件系统。
mkfs -t ext3 /dev/vdb3
umount:取消挂载
非常简单,如下
umount hello/ # 方式一
umount /dev/vdb4 # 方式二
fdisk:创建分区
命令比想的要简单。举例,腾讯云,挂了块10G的云盘,想要进行分区肿么弄?
假设该云盘对应的设备为/dev/vdb,那么可以fdisk /dev/vdb。接下来就是按照提示一步一步来了。
输入m,会给你各种选项。
[root@VM_70_229_centos data]# fdisk /dev/vdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help):
比如可以通过p输出当前的分区情况
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/vdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes, 20971520 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xeb9c2fe3
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/vdb2 4196352 20971519 8387584 5 Extended
/dev/vdb4 2048 4196351 2097152 83 Linux
/dev/vdb5 4198400 8392703 2097152 83 Linux
Partition table entries are not in disk order
Command (m for help):
如果要新增分区的话,可以通过n命令。分区类型的注意事项:
- 默认:最多四个分区,分区类型可以是primary、extended
- 需要超过4个分区:可以将其中一个分区的类型选择为extended,然后在该extended分区的基础上继续进行分区。
- 逻辑分区:在extended分区的基础上分出来的区,就是逻辑分区啦。
- primary、logical分区能格式化,extended分区不能格式化。
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 1 extended, 2 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
编辑/etc/fstab:开机自动挂载分区
备注:下面是云主机生成时的启动挂载配置。
/dev/vda1 / ext3 noatime,acl,user_xattr 1 1
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs noauto 0 0
debugfs /sys/kernel/debug debugfs noauto 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts mode=0620,gid=5 0 0
照葫芦画瓢,把我们需要的开机挂载配置写进去,比如下面的内容,其中
- defaults:文件系统参数,一般用默认的就行。
- 第五栏:能否被 dump 备份命令作用:
- 第六栏:是否以 fsck 检验扇区:
/dev/vdb5 /data/github ext3 defaults 1 0